Portable Fire Extinguisher (PFE) is a tube containing high-pressure fire extinguisher material(s). As the name implies, PFE is used to extinguish or control fires on a small scale. From the Occupational Health and Safety point of view, a company is required to have PFE equipment to maintain the safety of its employees. When learning about PFE, it is crucial to know the different classes of fire and the types of fire extinguishers.
Classes of Fire
The differences in extinguishing materials in a PFE depend on the types of items that may be the fuel or source of fire in a building. Fires are divided into five classes:
Class A
Class A fires are the most common class among the other four. They are caused by the common combustible materials burned, such as wood, paper, clothing, and plastic.
Class B
Class B fires arise from the burning of flammable liquids and gases. Some Class B fire fuels are gasoline, oil, and paint. Because those fuels are easy to flow, Class B fires can spread rapidly.
Class C
Class C fires are propagated from the damage or defects in an electrical circuit, which are a spark, short circuit, or power surge. Usually, the source of fire for this class is in a remote or hidden area within a building.
Class D
Class D fires arise from the burning of flammable metals. Those metals include magnesium, titanium, sodium, potassium, and lithium.
Class K
Class K fire fuels are flammable materials or items in the kitchen. These include cooking oil and fats.
Types of Portable Fire Extinguisher
To use or install PFEs, we need to know the characteristics of each PFE type. Based on the extinguishing materials composition, PFEs are divided into four types: Water, Foam, Dry Chemicals, and Carbon Dioxide PFEs.
Water-Fire Extinguisher
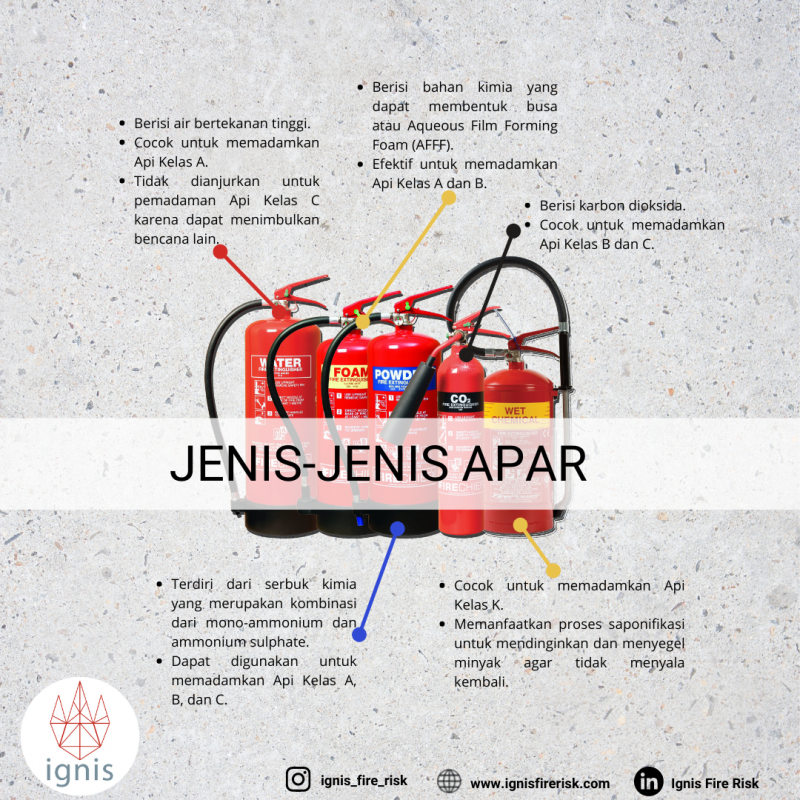
As the name suggests, this fire extinguisher uses high-pressured water as its extinguishing material. Water PFE is suitable for Class A fires and is not recommended for extinguishing Class C fires because they might cause other accidents/disasters.
Foam Fire Extinguisher
Foam PFEs use chemicals that can change their form into foam or Aqueous Film Forming Foam (AFFF) as an extinguishing agent. As result, some people call this type of PFE an AFFF fire extinguisher. Foam/AFFF PFE is very effective in extinguishing Class A and B fires.
Dry Chemical Fire Extinguisher
The dry chemical fire extinguisher uses the chemical powder that combines mono-ammonium and ammonium sulfate as its extinguishing materials. This fire extinguisher can be used for Class A, B, and C fires. Thus, many people also address this PFE as an ABC fire extinguisher.
Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Fire Extinguisher
As the name implies, this fire extinguisher uses carbon dioxide as its extinguishing material. The carbon dioxide will replace the oxygen around the fire. As a result, the fire will be extinguished due to lack of or running out of oxygen. This type of fire extinguisher is suitable for Class B and C fires.
Wet Chemical Fire Extinguisher
The wet chemical fire extinguisher can be used to extinguish Class K fires. The wet chemical and the oil will form a reaction, namely saponification which gives us soapy substances. This process cools down the surface of the oil and seals it so it would not re-ignite.
Figures 1. Types of PFE
PFEs Installation and Maintenance Requirements
In Indonesia, the standard for the installation and maintenance requirements of PFEs has been summarized in the Regulation of the Minister of Manpower and Transmigration No: PER.04/MEN/1980 concerning the Requirements for Installation and Maintenance Portable Fire Extinguishers. The standard installation for PFEs under the regulation are:
PFEs must be located in an easily accessible place. It means that there should not be any other objects that might prevent people from accessing the PFEs.
PFEs are mounted on the wall with an ideal height from the floor is 125 cm. However, the minimum height from the floor that must be fulfilled is 15 cm.
A sign with “PFE” written on it should be provided. The sign can be installed above the PFEs.
The distance between one PFE to another is 15 m.
If the PFEs are outside, they should be equipped with PFE boxes to prevent premature damage caused by extreme weather and direct sunlight exposure.
Each fire extinguisher is periodically tested no more than once every five years. Each fire extinguisher is considered feasible if it is able to withstand the respective test pressures.
PFEs Operational and Socialization
As stated earlier, fire extinguishers are effective in dealing with small-scale fires. However, PFEs might become useless if the occupants of a building do not know when and how to use them. Thus, a company needs to conduct socialization and training on the operation procedure of fire extinguishers for its employee.
How to Use PFEs
In using PFEs, there are four stages abbreviated as PASS:
- Pull. Pull out the fire extinguisher pin.
- Aim. Aim the nozzle at the fire source.
- Squeeze. Press the fire extinguisher handle.
- Sweep. Sweep from each side.
Writer: Fitri Endrasari - Fire Engineer Ignis Fire & Risk
Marvinjem
https://ultimelestiri.md/social/cum-o-companie-rusa-a-organizat-un-atac-cibernetic-asupra-unei-firme-din-r-moldova/#google_vignette