In planning the construction of a
building, fire safety management (FSM) is one of the crucial aspects that
should not be missed. Even so, many buildings in Indonesia are built without
considering this aspect because some parties are unaware of the importance of
fire safety management for buildings. As a result, many fires eventually became
massive and caused huge losses. Recently, on April 11, 2022, there was a fire
in the basement of the Bassura Apartment (TribunJakarta.com, April 11, 2022,
Bima Putra). The extinguishing process lasted longer (four hours) because the
firefighters also had to emit smoke using a smoke removal car.
This event resulted in IDR2.000.000.000,00 losses. If the fire safety management is adequate (including the smoke control system), the extinguishing process can be carried out faster, and losses can be minimized.
What is FSM?
Out of many management types, fire
safety management, or FSM, belongs to risk management. According to the Great
Dictionary of the Indonesian Language (KBBI), risk management is an effort to
reduce the impact of uncertainty elements. That's right, fires are part of the
uncertainty, as they can occur anytime and anywhere. FSM is an early management
system that plays a role in preventing and controlling fire hazards so that
losses in the form of life and materials can be prevented or minimized. This
can be done by striving for the readiness of fire protection installations so
that they always function and are ready to use.
In Indonesia, there are three laws that become the legal basis of FSM. Those laws are:
- Law No.1 of 1970 concerning Occupational Safety and Health
- Law of the Republic of Indonesia Number 28 of 2002 concerning Buildings
- Law No.24 of 2007 concerning Disaster Management
Elements of FSM
Indeed, we need to admit that preparing for FSM is not an easy matter. FSM is composed of several systems that can and must be implemented and explained in detail. The fire safety management system for actively operating buildings consists of seven systematic models or elements. Those elements are:
- Management
Commitment
Management commitment is the basis for the preparation of FSM. The management ranks can steer the organization toward the realization of FSM. Their decisions and behaviors play a crucial role in preventing various disasters or disturbances that may disrupt or even stop the activities in a building. More importantly, this management commitment must also consider the existing human resources (ensuring their safety in the event of a disaster).
- Baseline
Assessment
The baseline assessment aims to provide management with an overview of the latest condition of the relevant building safety aspects, including existing personnel data, systems (or procedures), and equipment. With these data, the management or building owner can find out the readiness of the building to face fires and use this information to carry out fire planning.
- Pre-Fire
Planning
Pre-fire planning
consists of four sub-elements, which are:
- Prevention
We can prevent fires by
identifying things that have the potential to initiate fires, both in terms of
fuel and fire sources. Once the potential ignition sources are identified, we
can make the prevention measures.
For example, an employee
who uses the stove in the office's kitchen cannot leave it while
it is on. If there is a gas leakage, the employee can have an early
identification. Thus, fires due to gas leaks can be prevented or minimized.
- Preparedness
At this stage, the
management will design a detailed plan related to the readiness of the building
in the face of fire.
Preparations also include
providing socialization and training to building occupants in extinguishing
fires on a small scale, fire drills, and preparing for fire management
cooperation.
- Response
When fires cannot be
avoided, the response of the occupants plays a vital role in controlling and
stabilizing the situation in the building.
In this process, there must be vivid coordination between the parties in
charge of the building. In addition, the
evacuation process must also be carried out as effectively as possible to minimize
the number of victims.
- Recovery
Recovery is a sub-element prepared to restore the function of the building. During this period, impact analysis and how to minimize it are required for effective and consistent recovery planning.
- Implementation
Implementation is the implementation stage of the pre-fire planning that has been made.
- Control
As long as the implementation is still carried out, supervision is needed to ensure that each element achieves the goals that have been set.
- Audit
The audit process is carried out to ensure that the system runs in accordance with the provisions and policies of the company.
- Management
Review
Of course, the FSM needs to be reviewed to ensure its contextuality. It is closely related to possible changes in the building function, facilities, or environment.
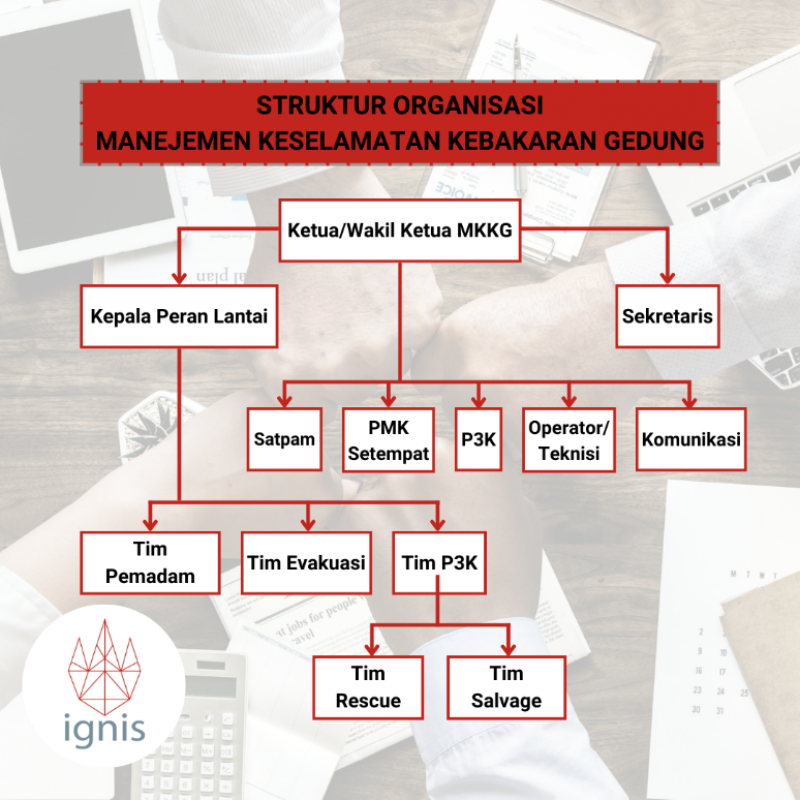
Hierarchy in FSM
In Indonesia, the minimum standard for the organizational structure of building fire safety management can be seen in the chart below:
https://ukrain-Forum.biz.ua
When I origginally left a comnent Iseem to have clicked on the -Notify me when new comments aree added- checkbox and from now on each time a comment is added I receive four emails with the same comment. There has to be a means you can remove me from that service? Kudos! https://ukrain-Forum.biz.ua